- today

Osteoporosis, the bone mass decrease, is a very common disease of the skeletal system, the metabolism of bone tissue. It leads to increased bone fragility and greater bone susceptibility to fractures. Due to the disruption of the microarchitecture in the bone tissue, the healing of fractures in patients with osteoporosis is often very complicated and takes a long time. The most common causes of osteoporosis are, for example, menopause, aging of the body, metabolic diseases, genetic factors, lifestyle factors, etc.
And how are our peptides related to osteoporosis?
Recent studies have shown that 4 peptides have positive healing effects on osteoporosis. They are BPC-157, AOD-9604, MOTS-c and the 11R-VIVIT peptide. In the following lines, we will take a closer look at the first two of them and the research that was carried out in this regard on animals.
Introducing the BPC-157 Peptide
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound - 157) is a pentadecapeptide formed from 15 amino acids. It is a synthetic amino acid sequence that resembles the naturally occurring complex in human gastric juice. Research has shown that BPC-157 helps in the healing of various types of wounds and tendons (including a ruptured Achilles tendon), accelerates the healing of burns, has an overall anti-inflammatory effect, promotes liver regeneration, digestion, protects the digestive organs, means a prevention against the formation of stomach ulcers and also regenerates tissues of GI tract. It can successfully regenerate tendons, ligaments, brain, bones, etc.
BPC-157 Against Osteoporosis
An animal study, specifically rats, demonstrated the effects of BPC-157 in possibly improving fracture and wound healing. The causes of osteoporosis are really different and the exact process and mechanism is still being researched and clarified. We can cite the example of gastrectomy, where osteoporosis, metabolic aberration and the risk of fractures may also occur. Therefore, the delivery of a gastric peptide with osteogenic activity is more than desirable. But let's get back to the BPC-157 peptide studies and how they went and what they found.
In another animal study, scientists investigated and demonstrated the effects of BPC-157 on rabbits. The rabbits had a segmental osteo periosteal bone defect that was untreated for 6 weeks in all control subjects. BPC-157 was administered continuously percutaneously intramuscularly directly into the bone defect site. Results were evaluated at 2-week intervals. Autologous bone marrow was applied locally percutaneously to rabbits for comparison. In standard treatment, the bone defect was filled with an autologous cortical graft immediately after it was created. Control subjects had wounds treated only with saline.
BPC-157 was shown to significantly improve the healing of segmental bone defects. For example, similar effects are seen after administration of BPC-157 as after local application of bone marrow or autologous cortical graft, according to radiography, callus surface, microphoto densitometry, quantitative histomorphometry (10 mg/kg body weight i.m. for 14 days) or (10 ng) /kg of body weight i.m. for 14 days).
In summary, intramuscular administration of BPC-157 provided results of effects comparable to administration of percutaneous injection of autologous bone marrow or autologous bone graft. Effects were also demonstrated after local application of BPC-157. In this way, the peptide could be the basis of the future solution of bone defects in complicated cases, whether the application would be intramuscular or local. Moreover, in toxicological tests, the peptide was shown to be apparently non-toxic, even at high doses. Thus, it turned out that the importance of the stomach for bone homeostasis is extremely great.
Peptide AOD-9604
AOD-9604 is a peptide fragment of growth hormone (GH) without proliferative effects that shows several effects on bone. It is an 8% fragment of the GH molecule that activates IGF-1, an insulin-like hormone, and also direct cellular pathways. However, AOD-9604 does not act on the IGF-1 pathway, which causes significant insulin resistance. This product is increasingly successfully used in the treatment of local pain: e.g. tendinitis, osteoarthritis, etc.
AOD-9604 Against Osteoporosis
In rabbits with collagenase-induced osteoarthritis of the knee, researchers from South Korea investigated the effects of intra-articular injections of AOD-9604, applied to the joint with or without hyaluronic acid (HA).
In the study, 32 adult New Zealand white rabbits were randomly given 2 mg of collagenase type II, twice in each knee joint. Subsequently, group 1 received weekly injections of 0.6 ml of saline, group 2 received 6 mg of hyaluronic acid, group 3 received 0.25 mg of AOD-9604, and group 4 received 0.25 mg of AOD-9604 together with 6 mg of hyaluronic acid. After the first intra-articular injection of collagenase, each injection was given for 4-7 weeks. The degree of cartilage degeneration was assessed using morphological and histopathological findings (see Figure 1). The degree of lameness was observed within 8 weeks of the first collagenase injection.
What were the results of the study and which group showed greater or minor symptoms on the cartilage?
The gross morphological and histopathological findings of the knee cartilage from the 4 different study groups are shown in Figure 1. Using this method to compare the results, the cartilage degeneration score was significantly higher in the saline-only group 1 than in groups 2, 3 and 4 and significantly lower in group 4, which received AOD-9604 plus hyaluronic acid, than in groups 2 and 3. The length of lameness in group 4, which received AOD-9604 + HA, was significantly shorter than in groups 1, 2, and 3 .The lameness period in group 1 was significantly longer than in groups 2 and 3.
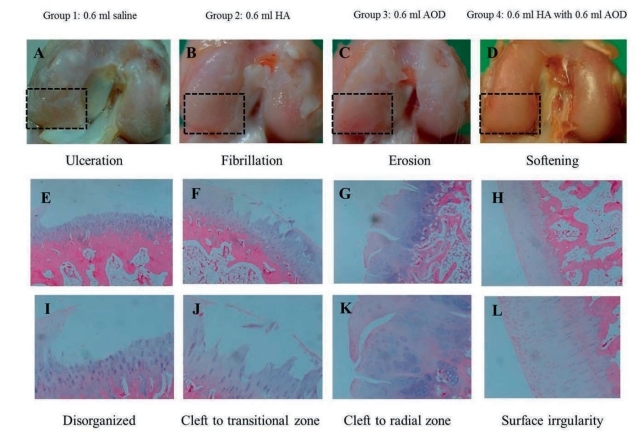
Figure 1:
Gross morphological (rectangular areas) and histological (hematoxylin and eosin stained, × 40 and × 100) findings of knee osteoarthritis in the four groups. Group 1: normal saline (A,E,I), group 2: hyaluronic acid (B,F,J), group 3: AOD-9604 (C,G,K), group 4: AOD-9604 together with acid hyaluronic (D, H, L).
Overall, it can be concluded that, according to the results of the study in rabbits with collagenase-induced osteoarthritis, intra-articular injections of AOD-9604, with the help of ultrasound guidance, improved the regeneration of knee cartilage. Furthermore, we can state that the combined injections of AOD-9604 with hyaluronic acid were more effective than the injection of hyaluronic acid or the AOD-9604 peptide applied alone.
Warning
THE GOODS OFFERED BY THE SELLER IS INTENDED FOR SCIENTIFIC AND DEVELOPMENT PURPOSES ONLY. The goods offered by the Seller include chemical substances that shall not be used as a drug, medicine, active substance, medical aid, cosmetic product, a substance for production of a cosmetic product neither for human consumption that is any food or food supplement or otherwise similarly used on humans or animals.
References: